Key Considerations When Choosing Between 3D Printing and Plastic Injection Molding
When deciding between 3D printing and plastic injection molding for your manufacturing needs, several key factors come into play. Production volume, part complexity, material requirements, and cost considerations all influence this critical choice. 3D printing shines for prototyping and small batches, offering design flexibility and quick turnaround. On the other hand, plastic injection molding excels in high-volume production, providing consistent quality and cost-effectiveness at scale. Understanding your project's unique demands and long-term goals is crucial in making the right decision. Let's explore the nuances of each method to help you determine the best fit for your production requirements.
Production Volume and Cost Analysis
Economies of Scale in Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is particularly advantageous for high-volume manufacturing due to its significant economies of scale. Although the initial investment in mold design and fabrication is relatively high, this cost is distributed across a large number of units as production volume increases. Consequently, the per-part cost decreases substantially, making injection molding a highly efficient and economical method for mass-producing consistent and high-quality parts. Industries such as automotive, consumer goods, and medical devices often rely on this process for orders ranging from thousands to millions of identical components.
3D Printing for Low-Volume and Customization
In contrast, 3D printing excels in low-volume production and scenarios requiring customization. Since it does not require the expensive tooling or molds associated with plastic injection molding, it significantly reduces upfront costs and lead time. This makes it ideal for prototyping, product testing, and small-batch manufacturing. Design changes can be implemented quickly and inexpensively, offering unparalleled flexibility. It is especially beneficial for industries like aerospace, healthcare, and custom consumer products, where unique designs and rapid iteration are critical.
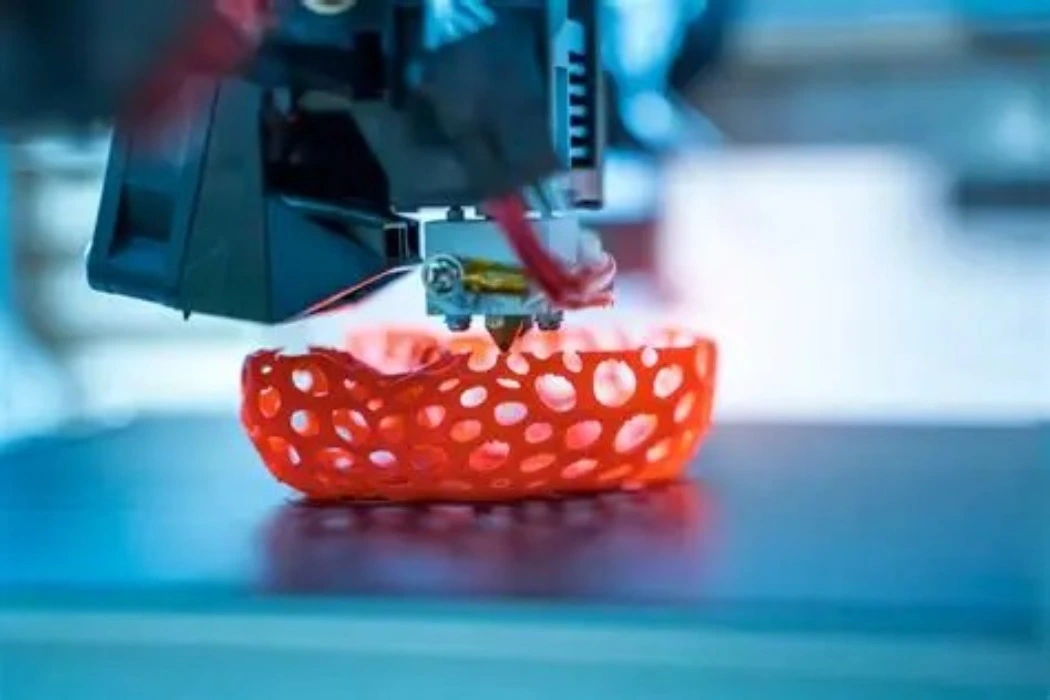

Break-Even Point Consideration
Identifying the break-even point between injection molding and 3D printing is essential for making a cost-effective decision. This point depends on factors such as part size, complexity, material selection, and production volume. Generally, injection molding becomes more economical at higher quantities due to lower per-unit costs, while 3D printing is preferable for smaller runs and complex, customized designs. A thorough break-even analysis helps manufacturers align their process choice with production goals and budget limitations.
Design Complexity and Material Selection
Geometric Freedom in 3D Printing
3D printing stands out for its exceptional capacity to produce highly complex geometries that are often unachievable through conventional manufacturing techniques. It supports the creation of intricate internal channels, organic shapes, and integrated assemblies in a single build process, eliminating the need for multi-part fabrication. This geometric flexibility is especially beneficial in sectors such as aerospace and medical implants, where optimized, lightweight, and custom components are essential for performance and functionality.
Material Limitations and Advancements
Although 3D printing materials have significantly diversified, plastic injection molding still provides a broader selection of polymers - including ABS, polypropylene, and engineering-grade plastics like PEEK - tailored to specific mechanical, thermal, or chemical requirements. Nevertheless, ongoing innovations in 3D printing, such as high-performance composites, ceramics, and multi-material printing, are progressively narrowing this gap and opening new application possibilities across various industries.
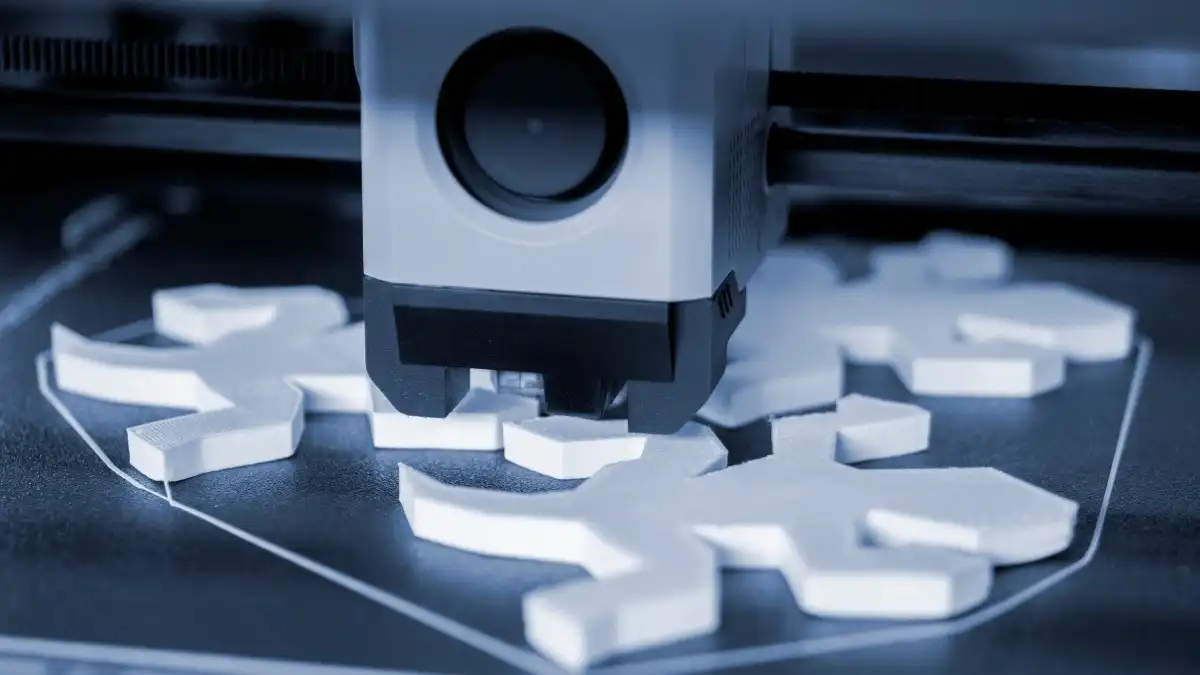

Surface Finish and Post-Processing
Parts produced via injection molding typically exhibit smooth surface finishes directly after demolding, reducing the need for extensive post-processing. In contrast, 3D printed parts often display layer lines or support marks, necessitating additional steps like sanding, polishing, or coating to achieve a similar aesthetic and functional quality. When selecting a manufacturing method, consider both the desired surface characteristics and available resources for finishing.
Time-to-Market and Production Flexibility
Rapid Prototyping Advantages
3D printing offers unparalleled speed in producing prototypes and small batches. This rapid turnaround is invaluable for testing designs, gathering feedback, and iterating quickly. It allows companies to validate concepts and make necessary adjustments before committing to large-scale production, potentially saving significant time and resources in the product development cycle.
Scalability of Injection Molding
Once a mold is created, plastic injection molding provides exceptional scalability. It can produce large volumes of parts quickly and consistently, making it ideal for mass production. This scalability is crucial for businesses looking to meet high demand or scale their production as their market grows. The ability to produce thousands of parts per day with minimal variation is a key advantage of plastic injection molding.
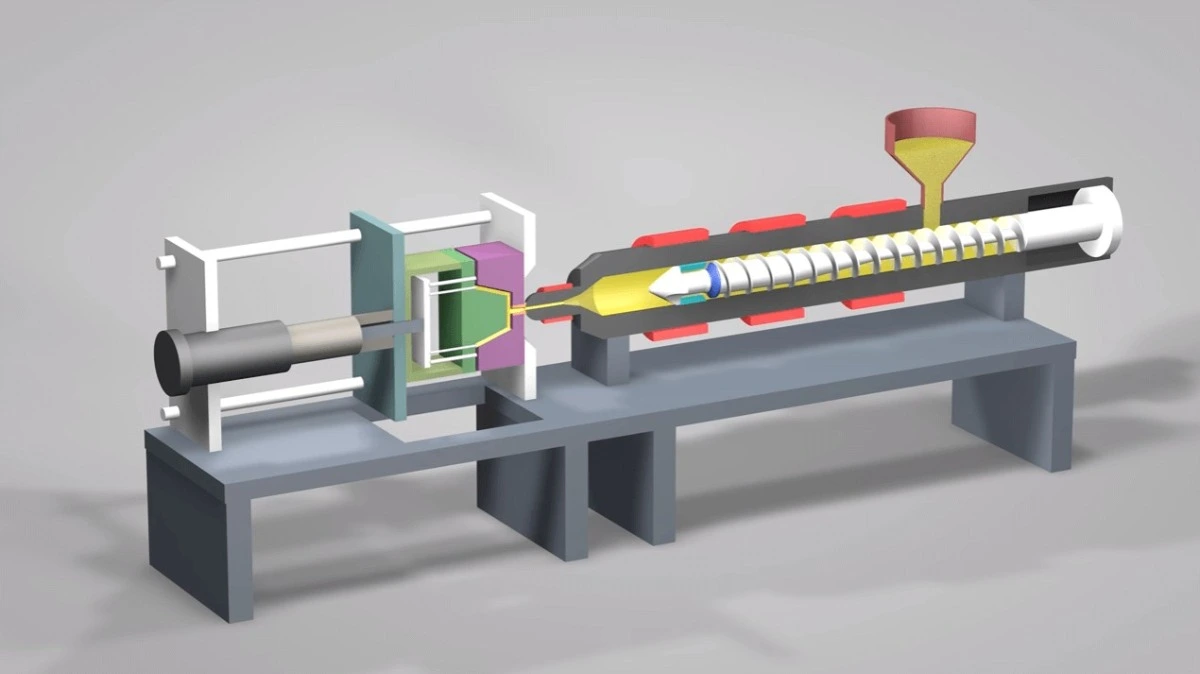
Adapting to Market Demands
The choice between 3D printing and injection molding can significantly impact a company's ability to respond to market changes. 3D printing offers the flexibility to quickly adjust designs or produce small batches of customized products. Injection molding, while less flexible, provides the stability and efficiency needed for established products with steady demand. Balancing these factors is essential in developing a responsive and efficient manufacturing strategy.
Conclusion
Choosing between 3D printing and plastic injection molding requires careful consideration of various factors including production volume, design complexity, material requirements, and time-to-market needs. While 3D printing offers unparalleled flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities, injection molding remains the king of high-volume, consistent production. The decision ultimately depends on your specific project requirements, long-term production goals, and budget constraints. By carefully weighing these factors, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your manufacturing needs and business objectives.
FAQs
What's the main difference between 3D printing and injection molding?
3D printing builds objects layer by layer, ideal for prototypes and small batches, while injection molding uses molds for high-volume production of identical parts.
Which method is more cost-effective?
3D printing is more cost-effective for small batches, while injection molding becomes more economical for large-scale production.
Can 3D printing match the quality of injection molding?
While 3D printing quality has improved, injection molding often provides superior surface finish and consistency, especially for high volumes.
Expert Plastic Injection Molding Services | BOEN
At BOEN, we specialize in high-quality plastic injection molding services tailored to your unique manufacturing needs. Our state-of-the-art facility and expert team ensure precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for projects of all scales. From prototyping to mass production, we deliver exceptional results with a wide range of materials and finishes. Experience the BOEN difference in plastic injection molding. Contact us at contact@boenrapid.com for a free quote and let's bring your vision to life.
References
1. Johnson, A. (2022). "Additive Manufacturing vs. Injection Molding: A Comprehensive Comparison". Journal of Manufacturing Technology, 15(3), 45-62.
2. Smith, B. & Lee, C. (2023). "Material Advancements in 3D Printing and Injection Molding". Advanced Materials Today, 8(2), 112-128.
3. Thompson, M.K. et al. (2021). "Design for Additive Manufacturing: Trends, opportunities, considerations, and constraints". CIRP Annals, 70(2), 701-724.
4. Wang, X. (2022). "Cost Analysis of 3D Printing and Injection Molding for Medium-Scale Production". International Journal of Production Economics, 235, 108080.
5. Garcia, E. & Patel, R. (2023). "Sustainability Comparison: 3D Printing vs. Traditional Manufacturing Methods". Journal of Cleaner Production, 330, 129751.
6. Brown, L. (2021). "Time-to-Market Strategies in Product Development: The Role of Rapid Prototyping". Innovation Management Journal, 12(4), 78-95.

How Can We Help?

Your Trusted Partner in Rapid Manufacturing.



