Exploring Traditional Low-Volume Manufacturing Techniques
CNC Machining: Precision and Versatility
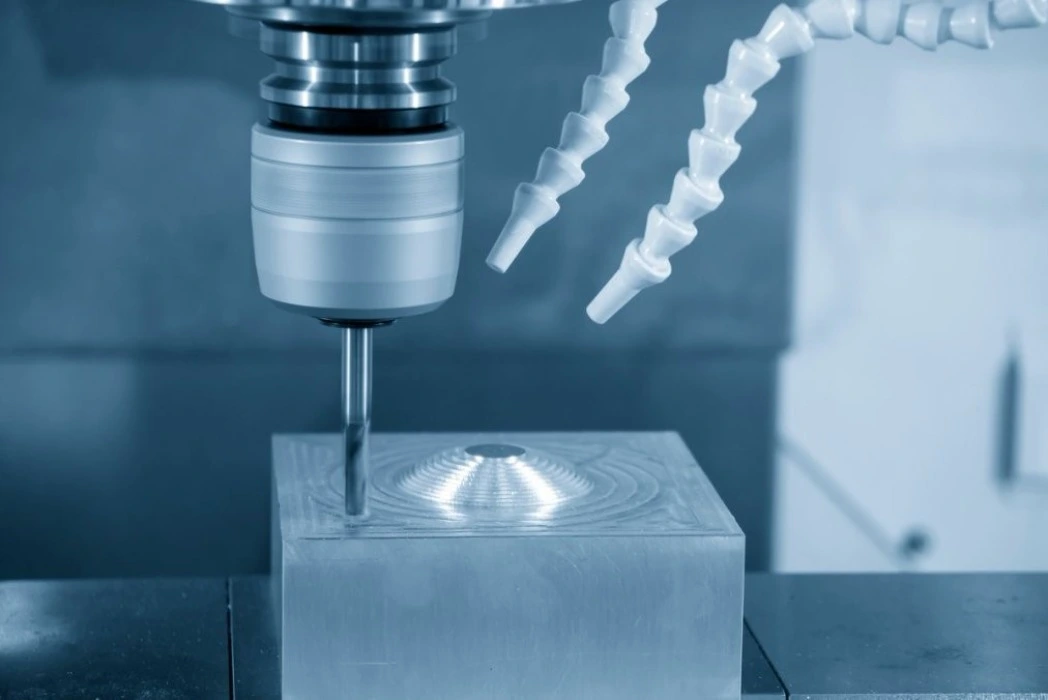
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a versatile subtractive manufacturing process ideal for low-volume production of metal and plastic parts. It can operate with a variety of materials and provides excellent precision. Tight tolerances and complicated geometries are two areas where CNC machining excels. Small to medium batches of parts with consistent quality can be produced effectively using this technology.
Injection Molding for Small Batches
While traditionally associated with high-volume production, injection molding can be adapted for low-volume manufacturing through rapid tooling techniques. This process involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity to create parts. For small batches, aluminum molds or 3D printed molds can be used to reduce costs and lead times. Injection molding offers excellent surface finish and is suitable for a variety of plastics and some metals.
Sheet Metal Fabrication Techniques
Creating things from metal sheets using a variety of techniques, including cutting, bending, and welding, is known as sheet metal fabrication. This process works especially well for producing enclosures, brackets, and other structural elements in small quantities. Rapid turnaround times and the production of intricate shapes with cheap tooling costs are made possible by techniques like laser cutting and CNC punching.
Innovative Technologies Revolutionizing Low-Volume Production
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has revolutionized low-volume production. This technology builds parts layer by layer, allowing for complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. Techniques like Stereolithography (SLA) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) offer high-quality results for various materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics. 3D printing is particularly advantageous for producing customized parts or small batches without the need for expensive tooling.
Vacuum Casting for Rapid Prototyping
A great technique for creating tiny quantities of plastic parts with characteristics comparable to injection-molded parts is vacuum casting. Using a master template, a silicone mold is made, and parts are then cast in a vacuum atmosphere.It's perfect for low-volume manufacturing, creating 10 to 100 parts and offers a cost-effective arrangement for prototyping or little generation runs, particularly when high-quality surface wraps up are required.
Advanced Die Casting Techniques
Die casting, while traditionally used for high-volume production, has been adapted for low-volume manufacturing through rapid tooling techniques. Melted metal is injected under high pressure into a mold cavity in this procedure. Rapidly made steel molds or aluminum molds can be used for small batches. Die casting is appropriate for companies needing robust, high-quality components in smaller quantities because it provides exceptional dimensional accuracy and surface finish for metal parts.
FAQ
What is low-volume manufacturing and when is it used?
Low-volume manufacturing refers to producing small quantities of parts - typically between 10 and 10,000 units. It's ideal for prototyping, market testing, custom products, or bridging the gap between prototype and full-scale production.
What are the main advantages of low-volume manufacturing?
This method offers faster turnaround times, reduced tooling costs, and greater flexibility in design changes. It lowers financial risk, supports rapid innovation, and helps businesses respond quickly to market feedback.
Which low-volume manufacturing methods are best for metal parts?
CNC machining, die casting, and metal 3D printing (such as DMLS or SLM) are popular for low-volume metal parts. They deliver high precision, good surface finish, and material versatility across various industries.
How does 3D printing support low-volume manufacturing?
3D printing enables fast production of complex parts without tooling, making it cost-effective for short runs. Technologies like SLA and SLS are widely used for custom components, functional testing, and end-use applications.
Conclusion
For companies wishing to fabricate high-quality components and items in littler amounts, low-volume fabricating procedures give a assortment of choices. Every technology, from cutting-edge methods like 3D printing and vacuum casting to more conventional ones like CNC machining and injection molding, has special benefits. Manufacturers can balance aspects like cost, quality, and production time by knowing these different approaches and selecting the one that best suits their needs. Low-volume manufacturing will surely change as technology develops further, providing even more effective and adaptable options for companies of all kinds.

Low-Volume Production with Fast Lead Times | BOEN
At BOEN Prototype, we specialize in delivering high-quality prototypes and low-volume production in both plastic and metal materials. Automotive, robotics, medical devices, aerospace, defense, consumer electronics, and agricultural are just a few of the many areas in which we have experience. We take great satisfaction in our ability to deliver quick turnaround times without sacrificing quality. CNC machining, Rapid Injection Molding, Compression Molding, Metal Pressing, Die Casting, Vacuum Casting, and several 3D printing technologies including SLA and SLS are all part of our extensive manufacturing capabilities. Our profound knowledge of materials and integrated production processes, which enables us to address even the most challenging manufacturing problems, is what distinguishes BOEN. For more information about our services and how we can support your product development needs, please contact us at contact@boenrapid.com.






