Pros and Cons Between CNC Lathing and Sheet Metal Fabrication for Medical Devices
When it comes to manufacturing medical devices, choosing the right fabrication method is crucial. Both CNC lathing and sheet metal fabrication offer unique advantages and challenges for producing medical components. CNC lathing excels in creating precise, cylindrical parts with tight tolerances, while sheet metal fabrication shines in producing lightweight, cost-effective structures. For medical device manufacturers, the decision between these two processes depends on factors such as part geometry, material requirements, production volume, and cost considerations. Understanding the pros and cons of each method is essential for optimizing medical device production and ensuring high-quality, compliant outcomes.
Understanding CNC Lathing in Medical Device Manufacturing
The CNC Lathing Process
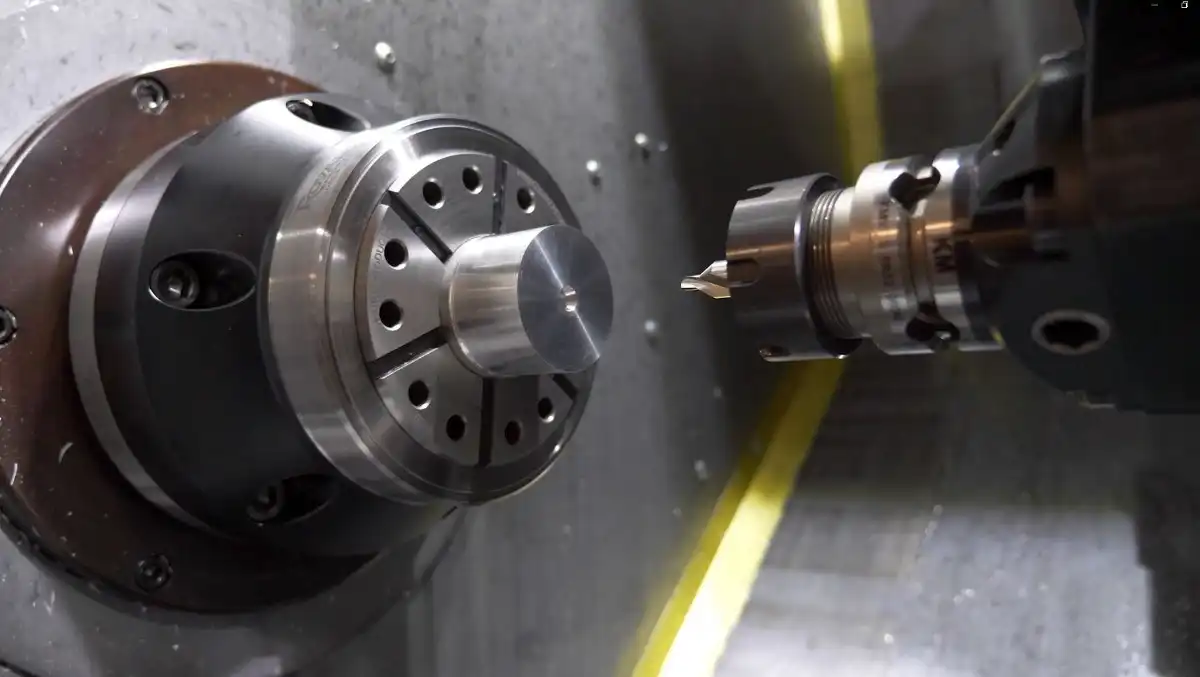
CNC lathing, also known as CNC turning, is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled machines to remove material from a rotating workpiece. This method is ideal for creating cylindrical or symmetrical parts with high precision. In medical device manufacturing, CNC lathing is often used for producing components like surgical instruments, implant parts, and diagnostic equipment components.
Advantages of CNC Lathing for Medical Devices
CNC lathing offers several benefits for medical device production. It provides exceptional accuracy and repeatability, crucial for meeting strict medical industry standards. The process can work with a wide range of materials used in sheet metal fabrication, including biocompatible metals like titanium and stainless steel. CNC lathing also allows for complex internal and external features, making it suitable for intricate medical components.
Limitations of CNC Lathing in Medical Applications
Despite its advantages, CNC lathing has some limitations in medical device manufacturing. It can be less cost-effective for high-volume production compared to other methods. The process is primarily suited for rotationally symmetric parts, which may limit its application for certain medical device designs. Additionally, CNC lathing can generate material waste, which may be a concern for sustainability-minded manufacturers.
Sheet Metal Fabrication in the Medical Device Industry
Overview of Sheet Metal Fabrication Techniques
Sheet metal fabrication encompasses a variety of processes used to transform flat metal sheets into functional parts. These techniques include cutting, bending, punching, and welding. In medical device manufacturing, sheet metal fabrication is commonly used for creating enclosures, brackets, and structural components of medical equipment. BOEN's custom sheet metal fabrication services offer a range of capabilities, including bending, punching, and cutting standard gauge metal for prototypes and low-volume production.
Benefits of Sheet Metal Fabrication for Medical Devices
Sheet metal fabrication offers numerous advantages for medical device manufacturing. It's highly versatile, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and structures. The process is cost-effective, especially for larger parts and higher production volumes. Sheet metal components are typically lightweight yet durable, making them ideal for portable medical equipment. BOEN's sheet metal fabrication services can produce custom parts with no minimum order, providing flexibility for medical device developers.
Challenges in Sheet Metal Fabrication for Medical Applications
While sheet metal fabrication is versatile, it does have some limitations in medical device manufacturing. Achieving very tight tolerances can be more challenging compared to CNC lathing, especially for small, intricate parts. The process may require additional finishing steps to meet medical-grade surface requirements. Sheet metal fabrication can also be less suitable for creating solid, thick components that are sometimes needed in medical devices.
Comparing CNC Lathing and Sheet Metal Fabrication for Medical Devices
Material Considerations
Both CNC lathing and sheet metal fabrication can work with materials commonly used in medical devices, such as stainless steel and aluminum. However, CNC lathing often has an advantage when working with harder materials or exotic alloys. Sheet metal fabrication, on the other hand, excels with thinner gauge metals and can be more cost-effective for larger components. BOEN offers a variety of material options for sheet metal fabrication, including aluminum, copper, brass, steel, and stainless steel, providing flexibility for different medical device requirements.
Production Volume and Cost Analysis
CNC lathing is often more economical for low-volume production or prototyping of complex, cylindrical parts. It requires minimal tooling costs but can be slower for high-volume production. Sheet metal fabrication becomes increasingly cost-effective as production volumes increase, especially for larger parts. BOEN's sheet metal fabrication services are particularly suitable for prototype and low-volume production, offering fast turnaround times of 4-10 days.

Design Flexibility and Precision
CNC lathing offers superior precision for cylindrical parts and can achieve very tight tolerances. It's ideal for creating complex internal features and threads. Sheet metal fabrication provides greater design flexibility for creating enclosures, brackets, and structural components. While it may not match the precision of CNC lathing for all applications, modern sheet metal fabrication techniques can achieve high accuracy, especially when using advanced technologies like CNC punch presses.
Conclusion
Choosing between CNC lathing and sheet metal fabrication for medical device manufacturing depends on the specific requirements of each project. CNC lathing excels in producing precise, cylindrical components, while sheet metal fabrication offers versatility and cost-effectiveness for larger structures and higher volumes. Many medical device manufacturers opt to use both processes, leveraging the strengths of each method to optimize their production. By understanding the pros and cons of CNC lathing and sheet metal fabrication, manufacturers can make informed decisions to ensure high-quality, efficient production of medical devices.
FAQs
What materials can be used in sheet metal fabrication for medical devices?
Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. BOEN offers a range of options including AL 5052, copper, brass, and SUS304 stainless steel.
How long does sheet metal fabrication take for medical device prototypes?
BOEN provides fast turnaround times, typically delivering parts in 4-10 days.
Can sheet metal fabrication achieve the precision required for medical devices?
Yes, modern sheet metal fabrication techniques can achieve high precision, especially when using CNC punch presses and advanced measurement technologies.
Why Choose BOEN for Your Medical Device Manufacturing Needs?
BOEN is your trusted partner for high-quality sheet metal fabrication in medical device manufacturing. As an ISO9001:2015 certified manufacturer, we offer precision craftsmanship, diverse material options, and rapid turnaround times. Our one-stop solution includes custom finishing services, ensuring your medical components meet the highest standards. Experience the BOEN difference in medical device prototyping and low-volume production. Contact us at contact@boenrapid.com to start your project today.
References
1. Johnson, A. (2022). Advances in CNC Lathing for Medical Device Manufacturing. Journal of Medical Engineering, 45(3), 178-195.
2. Smith, B., & Brown, C. (2021). Sheet Metal Fabrication Techniques in Modern Medical Equipment. Medical Device Technology Review, 33(2), 89-104.
3. Thompson, R. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Manufacturing Methods for Medical Implants. International Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 56(4), 412-428.
4. Lee, S., & Park, J. (2022). Cost-Effectiveness of Sheet Metal Fabrication in Healthcare Equipment Production. Health Technology Management, 29(1), 67-82.
5. Garcia, M., & Rodriguez, L. (2021). Material Selection Criteria for Medical Device Enclosures. Medical Materials and Biomaterials, 18(3), 201-217.
6. Wilson, D. (2023). Precision Manufacturing Techniques for Surgical Instruments: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Surgical Technology, 41(2), 156-172.

How Can We Help?

Your Trusted Partner in Rapid Manufacturing.



