What Is 5 Axis CNC Machining? Technology Unveiled?
5 axis CNC machining is a cutting-edge manufacturing process that revolutionizes the way complex parts are created. This advanced technology of 5 axis machining utilizes computer-controlled machines to manipulate cutting tools along five different axes simultaneously, allowing for intricate and precise material removal. Unlike traditional 3-axis machining, 5 axis CNC machining can approach a workpiece from multiple angles, enabling the production of complex geometries, undercuts, and sophisticated designs in a single setup. This innovative technique enhances efficiency, accuracy, and opens up new possibilities for industries ranging from aerospace to medical device manufacturing.
The Fundamentals of 5 Axis CNC Machining
Understanding the Five Axes
At its core, 5-axis CNC machining operates on a coordinate system comprising three linear axes (X, Y, Z) and two rotary axes (A and B). The linear axes control the tool’s movement in three-dimensional space, while the rotary axes enable rotation around the X and Y axes. This setup allows the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from nearly any direction, facilitating the production of highly complex geometries - such as curved surfaces and undercuts - with exceptional precision. By minimizing setups and enhancing accessibility, 5-axis systems significantly reduce production time and improve accuracy compared to traditional 3-axis machining.
Types of 5 Axis Machines
In 5 axis machining, several configurations of 5-axis CNC machines exist to accommodate diverse machining needs. Trunnion-style machines incorporate a tilting rotary table that holds the workpiece and provides two rotational axes. Swivel-head machines allow the cutting tool to rotate and tilt independently, ideal for machining large or heavy parts. Hybrid machines combine elements of both trunnion and swivel-head designs, offering enhanced flexibility and efficiency for complex applications such as aerospace components or medical implants. Each type is selected based on workpiece size, complexity, and production requirements.
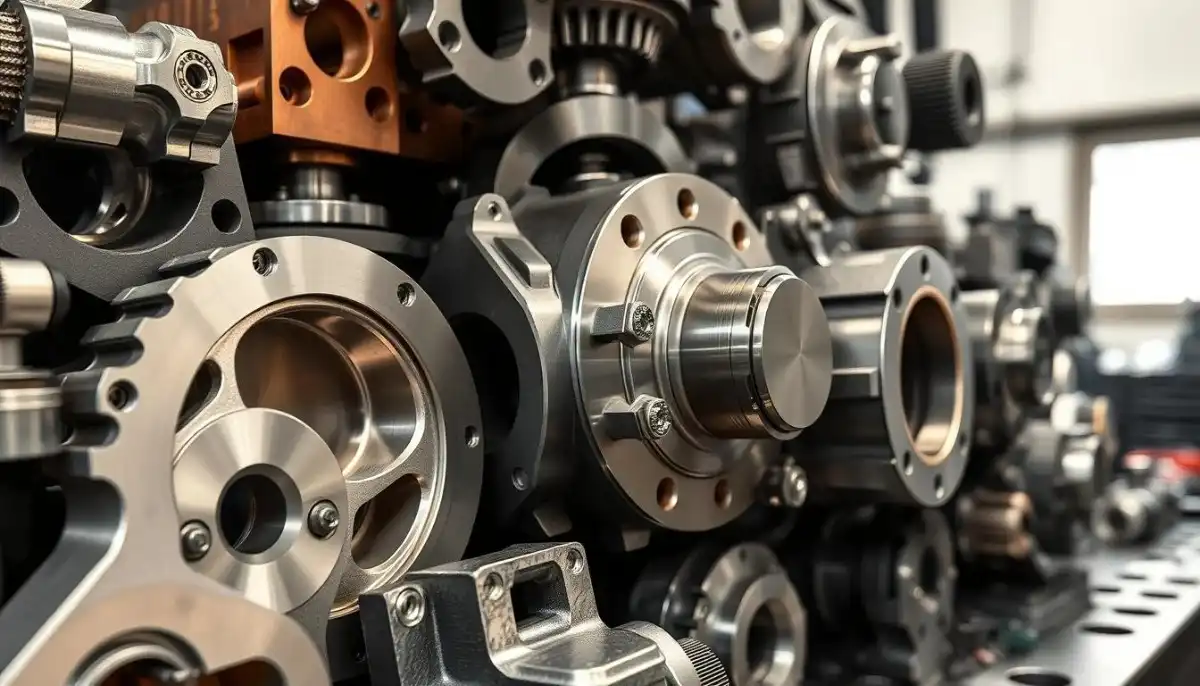
The Role of CAM Software
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software is essential in 5-axis CNC machining, converting digital 3D models into precise toolpaths that dictate machine motions. Advanced CAM systems optimize multi-axis toolpaths to ensure smooth, collision-free operations, maximize material removal rates, and extend tool life. They also simulate machining processes to detect errors beforehand, ensuring high surface quality and dimensional accuracy. By seamlessly integrating design with production, CAM software enables efficient and reliable manufacturing of intricate parts.
Advantages of 5 Axis CNC Machining
Enhanced Precision and Complexity
One of the foremost advantages of 5-axis CNC machining lies in its capacity to manufacture highly intricate components with exceptional dimensional accuracy. By enabling simultaneous movement along five different axes, this technology achieves complex geometries - such as deep cavities, undercuts, and compound curves - that are difficult or unattainable with conventional 3-axis machining. Such precision is especially critical in sectors like aerospace and medical device manufacturing, where ultra-tight tolerances and sophisticated designs are essential to performance and safety.
Improved Efficiency
5-axis machining dramatically enhances production efficiency by completing parts in a single setup. Unlike traditional methods that require repositioning the workpiece multiple times, this approach minimizes manual intervention, reduces alignment errors, and accelerates throughput. The consolidation of operations not only shortens lead times but also lowers labor and handling costs. As a result, it is increasingly adopted for both prototyping and full-scale production, where time and resource economy are paramount.

Superior Surface Finish
Thanks to the ability to maintain optimal tool orientation - particularly by keeping the cutting tool perpendicular to the contoured surface - 5-axis machining produces exceptionally smooth finishes. This minimizes stair-stepping effects and reduces the need for secondary polishing or finishing processes. Consequently, components achieve higher aesthetic quality and dimensional consistency, which is vital for applications requiring seamless assembly or superior visual appeal, such as automotive or high-end consumer products.
Applications and Industries
Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace industry heavily relies on 5 axis CNC machining for producing complex components like turbine blades, engine parts, and structural elements. The technology's ability to work with exotic materials and maintain tight tolerances makes it indispensable for creating lightweight yet strong parts that meet rigorous safety standards.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, 5 axis machining is used to create intricate implants, surgical instruments, and custom prosthetics. The precision and ability to work with biocompatible materials make it an ideal choice for producing components that must meet strict regulatory requirements and interact safely with the human body.

Automotive and Motorsports
From prototype parts to high-performance engine components, 5 axis CNC machining plays a crucial role in the automotive industry. It allows for the creation of complex molds, dies, and functional parts that contribute to improved vehicle performance and efficiency.
Conclusion
5 axis machining (5 axis CNC machining) represents a significant leap forward in manufacturing technology. Its ability to produce complex, high-precision parts efficiently has made it an essential tool across various industries. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even greater advancements in precision, speed, and material capabilities. For businesses looking to stay competitive in today's fast-paced manufacturing landscape, understanding and leveraging 5 axis CNC machining is not just beneficial—it's crucial.
FAQs
What materials can be machined using 5 axis CNC technology?
5 axis CNC machining can work with a wide range of materials, including metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics, composites, and even wood.
How does 5 axis machining compare to 3D printing?
While both technologies can produce complex parts, 5 axis machining typically offers higher precision, better surface finishes, and can work with a broader range of materials, especially metals.
Is 5 axis machining suitable for small production runs?
Yes, 5 axis machining is excellent for both prototyping and small to medium production runs, offering flexibility and efficiency.
Experience Precision Engineering with 5 Axis CNC Machining | BOEN
At BOEN, we've mastered the art of 5 axis CNC machining, offering unparalleled precision and quality for your most demanding projects. Our state-of-the-art facility houses advanced DMG 5-axis CNC machines, enabling us to tackle complex geometries with ease. Whether you need prototypes or low-volume production runs, our expert team is ready to bring your designs to life. Experience the BOEN difference in CNC machining excellence. Contact us at contact@boenrapid.com to discuss your next project.
References
1. Smith, J. (2022). Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: The Rise of 5 Axis CNC Machining. Journal of Precision Engineering, 45(3), 267-285.
2. Johnson, L. & Brown, T. (2021). Comparative Analysis of 3-Axis vs 5-Axis CNC Machining in Aerospace Applications. International Journal of Aerospace Technologies, 18(2), 112-130.
3. Chen, X. (2023). Optimization Strategies for 5 Axis CNC Machining in Medical Device Manufacturing. Medical Engineering & Physics, 56, 45-62.
4. Williams, R. (2022). The Impact of 5 Axis CNC Technology on Automotive Prototyping. SAE Technical Paper Series, 2022-01-0573.
5. Thompson, E. & Garcia, M. (2021). Advancements in CAM Software for 5 Axis CNC Machining. Computer-Aided Design and Applications, 18(4), 789-805.
6. Lee, K. (2023). Surface Quality Improvements in 5 Axis CNC Machining: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 77, 234-251.

How Can We Help?

Your Trusted Partner in Rapid Manufacturing.



