The Fundamentals of CNC Milling
How CNC Milling Works
CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process that employs rotating cutting tools to progressively remove material from a solid workpiece, shaping it into a custom-designed part. Operated by computerized controls, the machine precisely follows instructions from a CAD/CAM-generated program, guiding the tool along multiple axes—such as X, Y, and Z—to achieve high accuracy and complex geometries. This method is valued for its efficiency and versatility, accommodating everything from rapid prototyping to full-scale production. It supports a broad spectrum of materials, including metals like aluminum and steel, plastics such as ABS and nylon, as well as composites, making it essential in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
Types of CNC Milling Machines
Various types of CNC milling machines are available, each engineered for specific applications and operational requirements. Vertical milling machines feature a vertically oriented spindle that moves up and down, ideal for plunge-cutting and die-sinking tasks. In contrast, horizontal milling machines have a horizontal spindle arrangement, better suited for heavy-duty milling and larger production volumes. More advanced multi-axis systems, including 4-axis and 5-axis mills, allow for rotational movement in addition to linear travel, enabling the production of highly intricate components in a single setup without repositioning the workpiece. These capabilities reduce errors and shorten production time for complex parts.
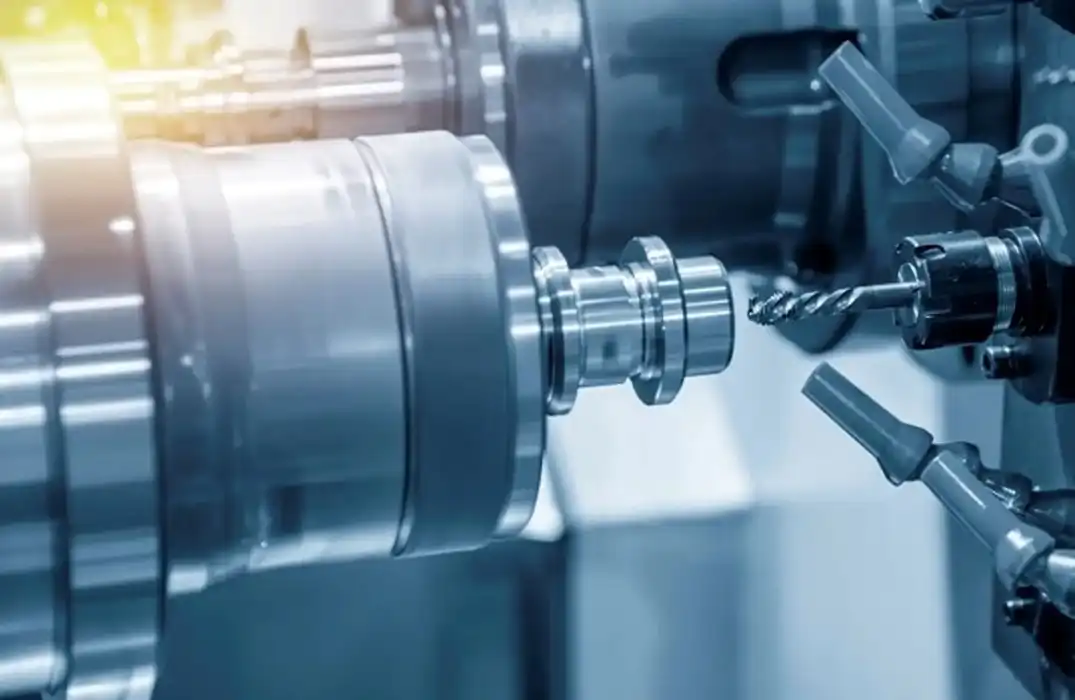

Key Components of a CNC Milling System
A complete CNC milling system comprises several integral components that ensure precision and functionality. The machine itself includes the spindle, which rotates the cutting tool; the worktable, which secures the workpiece; and mechanical elements that facilitate movement across multiple axes. The control unit contains a computer that interprets digital CAD/CAM designs and converts them into electrical signals to drive motors and actuators. Additionally, a variety of interchangeable cutting tools—such as end mills, face mills, drills, and taps—are used to perform specific operations like contouring, slotting, or finishing. Together, these elements form a highly automated and adaptable manufacturing system.
Advantages and Applications of CNC Milling
Precision and Repeatability
One of the primary advantages of CNC milling is its ability to produce parts with exceptional precision and consistency. The computer-controlled nature of the process ensures that each part is manufactured to the same exacting standards, making it ideal for industries that require high levels of accuracy, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Versatility in Material and Design
CNC milling can work with a wide range of materials, from soft plastics to hardened steel. This versatility, combined with the ability to create complex geometries, makes it suitable for producing everything from prototype parts to production tooling. The technology can handle intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with manual machining methods.
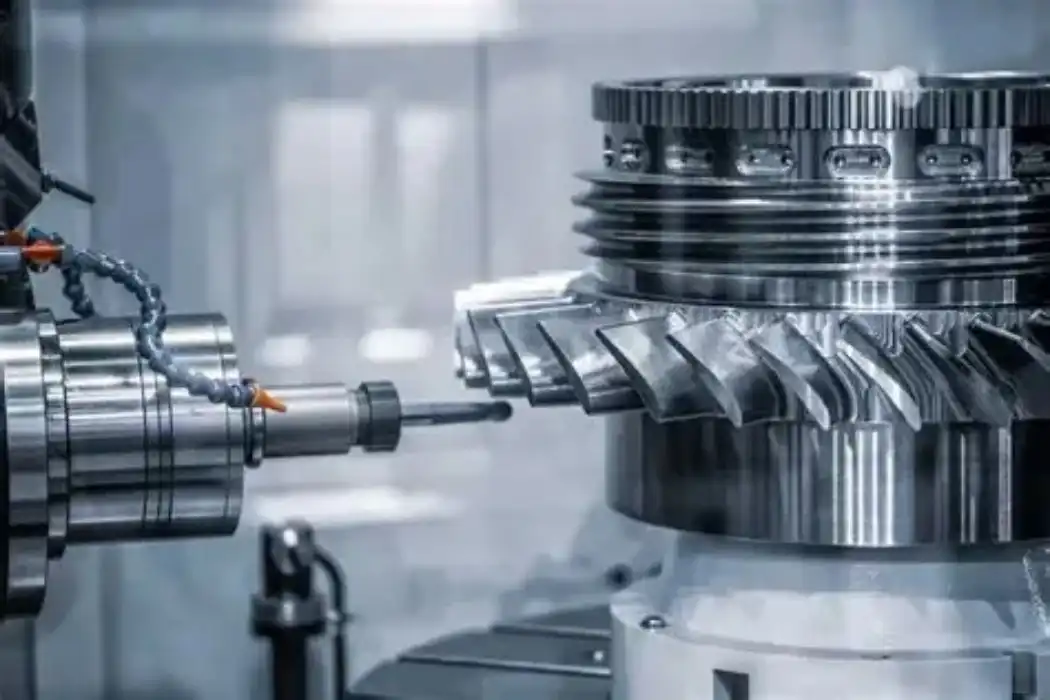
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in CNC milling equipment can be substantial, the technology offers significant long-term benefits in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness. CNC machines can operate for extended periods with minimal human intervention, reducing labor costs and increasing productivity. They also minimize material waste and can quickly switch between different projects, making them ideal for both small-batch and large-scale production.
The Future of CNC Milling
Integration with Industry 4.0
As manufacturing moves towards greater automation and connectivity, CNC milling is evolving to integrate with Industry 4.0 principles. This includes the incorporation of sensors for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance capabilities, and seamless integration with other manufacturing systems. These advancements are making CNC milling even more efficient and reliable.
Advancements in Software and Simulation
The software that drives CNC milling machines is becoming increasingly sophisticated. Advanced CAD/CAM programs now offer powerful simulation capabilities, allowing manufacturers to optimize toolpaths and identify potential issues before starting the actual machining process. This reduces setup time, minimizes errors, and improves overall efficiency.
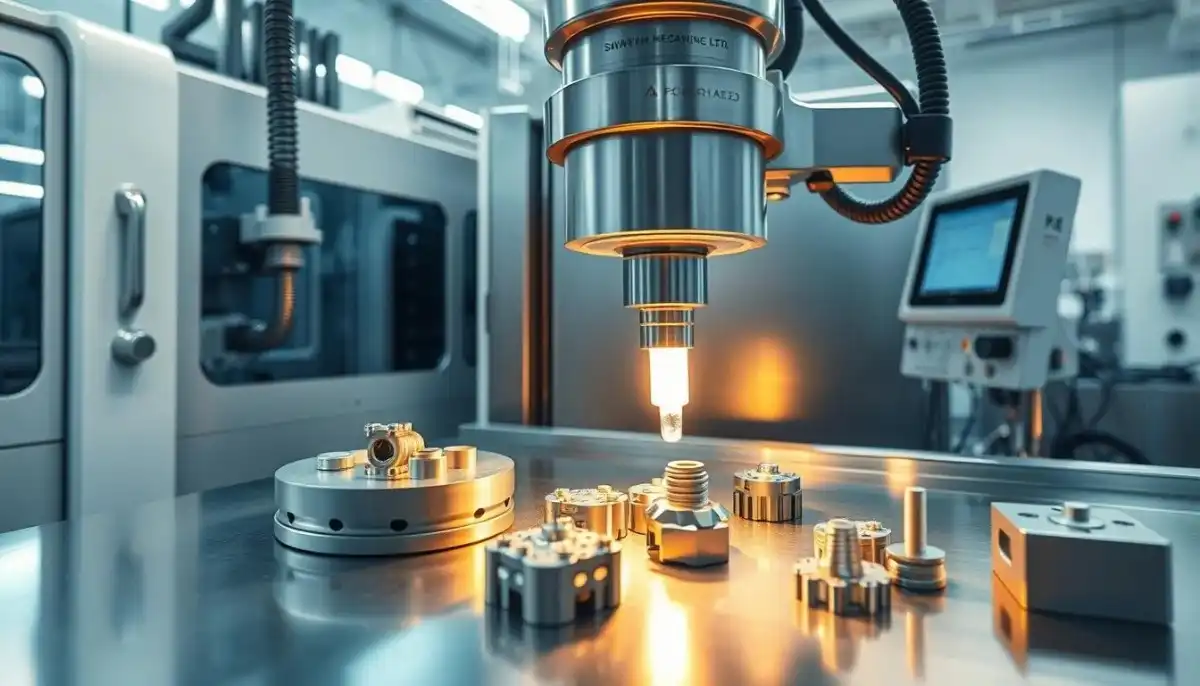
Hybrid Manufacturing Techniques
The future of CNC milling also includes its integration with other manufacturing technologies. Hybrid machines that combine CNC milling with additive manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing, are emerging. These machines offer the best of both worlds, allowing for the creation of complex parts that would be difficult to produce using either technology alone.
Conclusion
CNC milling has become an indispensable technology in modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, versatility, and efficiency. Its ability to produce complex parts with tight tolerances makes it crucial for industries ranging from aerospace to consumer electronics. As the technology continues to evolve, integrating with Industry 4.0 principles and other manufacturing techniques, CNC milling will remain at the forefront of innovation in production processes, enabling manufacturers to meet the increasingly demanding requirements of today's fast-paced, high-tech world.
FAQs
What materials can be used in CNC milling?
CNC milling can work with a wide range of materials, including metals like aluminum and steel, plastics, composites, and even wood.
How does CNC milling compare to 3D printing?
While 3D printing is additive, CNC milling is subtractive. CNC milling often offers better precision and can work with a wider range of materials, but 3D printing can create more complex internal structures.
What industries use CNC milling?
CNC milling is used in many industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, consumer electronics, and more.
Experience Precision CNC Milling Services | BOEN
At BOEN, we specialize in high-quality CNC milling for prototypes and low-volume production. Our advanced 3-, 4-, and 5-axis CNC machining centers, combined with our expertise in various materials, ensure precision and efficiency for your custom projects. From complex aerospace components to intricate medical devices, we deliver superior results. Contact us at contact@boenrapid.com to discuss your CNC milling needs with our skilled team.
References
1. Smith, J. (2022). Advanced CNC Milling Techniques for Precision Manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing Technology, 45(3), 287-302.
2. Johnson, A., & Brown, T. (2021). The Evolution of CNC Milling in Industry 4.0. Industrial Automation Quarterly, 18(2), 112-128.
3. Lee, S., et al. (2023). Comparative Analysis of CNC Milling and Additive Manufacturing in Aerospace Applications. Aerospace Engineering Review, 29(4), 401-418.
4. Williams, R. (2022). Optimizing CNC Milling Processes for Medical Device Manufacturing. Medical Technology Innovation, 14(1), 75-89.
5. Garcia, M., & Patel, K. (2021). Sustainability in CNC Machining: Reducing Waste and Energy Consumption. Journal of Sustainable Manufacturing, 7(3), 201-216.
6. Thompson, E. (2023). The Role of CNC Milling in Rapid Prototyping and Product Development. Product Design & Engineering, 33(2), 154-170.





