What Is CNC Turning? A Comprehensive Overview?
CNC turning is a sophisticated manufacturing process that combines precision engineering with computer-controlled automation. This versatile technique involves rotating a workpiece while a cutting tool removes material to create complex shapes and components. CNC turning excels in producing cylindrical parts with high accuracy and repeatability, making it ideal for a wide range of industries. From automotive to aerospace, medical devices to consumer electronics, CNC turning plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled efficiency and quality in part production.
The Fundamentals of CNC Turning
The CNC Turning Process Explained
At its core, CNC turning is a subtractive manufacturing method. The process begins with a solid piece of material, typically a cylindrical bar or rod, securely held in a chuck. As the workpiece rotates at high speeds, a cutting tool moves along various axes, precisely removing material to shape the desired part. This dynamic interplay between rotation and cutting allows for the creation of both simple and intricate geometries.
Modern CNC lathes are equipped with advanced features that enhance their capabilities. Tool turrets can hold multiple cutting tools, enabling quick changes for different operations. Live tooling allows for milling and drilling operations without removing the part from the lathe, increasing versatility and reducing production time.
Key Components of a CNC Turning Machine
A typical CNC turning center consists of several essential components:
- Spindle: The rotating element that holds and spins the workpiece.
- Chuck: Securely grips the material during machining.
- Turret: Holds multiple cutting tools for various operations.
- Tailstock: Provides additional support for long workpieces.
- Computer control system: Governs the entire operation based on programmed instructions.
- Coolant system: Manages heat and removes chips during cutting.
These components work in harmony to ensure precise, efficient, and repeatable part production. The computer control system, in particular, is the brain of the operation, interpreting complex G-code instructions to coordinate tool movements and machining parameters.
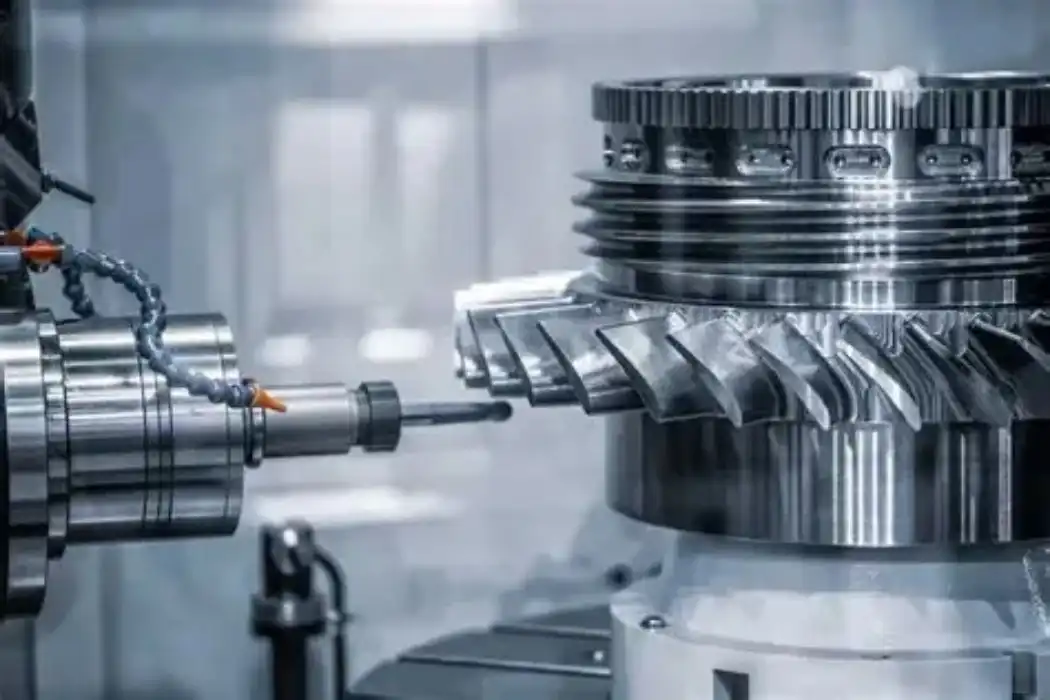
Materials Suitable for CNC Turning
CNC turning is remarkably versatile when it comes to material compatibility. Common materials include:
- Metals: Aluminum, steel, stainless steel, brass, copper, titanium
- Plastics: ABS, POM (Delrin), PTFE (Teflon), PEEK, nylon
- Exotic materials: Inconel, hastelloy, tungsten
The choice of material depends on the part's intended application, required properties, and cost considerations. Each material presents unique machining characteristics, influencing factors such as cutting speed, tool selection, and surface finish quality.
Advantages and Applications of CNC Turning
Benefits of CNC Turning in Manufacturing
CNC turning offers numerous advantages that make it a cornerstone of modern manufacturing:
- Precision and accuracy: Achieve tight tolerances consistently.
- Repeatability: Produce identical parts in large quantities.
- Complexity: Create intricate geometries and features.
- Efficiency: Reduce material waste and production time.
- Flexibility: Easily switch between different part designs.
- Cost-effectiveness: Ideal for both prototyping and high-volume production.
These benefits translate into improved product quality, reduced lead times, and enhanced competitiveness for manufacturers across various industries.
Industries Relying on CNC Turning
CNC turning finds applications in a wide array of sectors:
- Aerospace: Producing lightweight, high-strength components.
- Automotive: Manufacturing engine parts, shafts, and precision components.
- Medical: Creating implants, surgical instruments, and device components.
- Oil and Gas: Fabricating valves, fittings, and specialized equipment.
- Electronics: Producing connectors, heat sinks, and custom enclosures.
- Defense: Manufacturing critical components for military equipment.
The versatility of CNC turning makes it indispensable in these industries, where precision, reliability, and efficiency are paramount.

Common Parts Produced by CNC Turning
CNC turning excels in creating a diverse range of parts:
- Shafts and axles
- Bolts and fasteners
- Gears and sprockets
- Bushings and sleeves
- Valve components
- Custom fittings and connectors
- Threaded components
- Tapered parts and pins
These components often serve critical functions in larger assemblies, making the precision of CNC turning crucial for overall product performance and reliability.
Advanced Techniques and Future Trends in CNC Turning
Multi-Axis CNC Turning
Traditional CNC turning typically involves two axes of motion: X and Z. However, advanced multi-axis turning centers incorporate additional axes, such as Y-axis and B-axis capabilities. This expansion allows for more complex geometries and reduces the need for secondary operations.Multi-axis turning enables:
- Off-center drilling and milling
- Angled cuts and features
- Simultaneous turning and milling operations
- Reduced setup times and improved accuracy
These capabilities blur the line between turning and milling, creating highly versatile machining centers that can handle a wider range of part geometries and features.
Integration of Automation and Robotics
The future of CNC turning lies in increased automation and integration with robotic systems. This trend is driven by the need for higher productivity, consistency, and round-the-clock operation. Automated material handling systems, robotic tool changers, and in-process inspection systems are becoming more common in modern CNC turning setups.Benefits of automation in CNC turning include:
- Reduced labor costs
- Increased machine utilization
- Improved part consistency
- Enhanced safety for operators
- Flexibility to handle varying production volumes
As these systems become more sophisticated and affordable, even smaller manufacturers are beginning to adopt automated CNC turning solutions to stay competitive.

Advancements in Cutting Tools and Materials
Ongoing research and development in cutting tool technology and materials science continue to push the boundaries of what's possible in CNC turning. Some notable advancements include:
- Nano-structured coatings for enhanced tool life
- Cryogenic cooling techniques for improved heat management
- Ceramic and cubic boron nitride (CBN) tools for high-speed machining
- Additive manufacturing of custom cutting tools
- Development of new, more machinable alloys and composites
These innovations allow for faster cutting speeds, improved surface finishes, and the ability to machine increasingly challenging materials. As a result, CNC turning continues to evolve, meeting the ever-growing demands of modern manufacturing.
Conclusion
CNC turning stands as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility. From its fundamental principles to advanced multi-axis techniques, CNC turning continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and industry demands. As we look to the future, the integration of automation, robotics, and cutting-edge materials promises to further enhance the capabilities of CNC turning. For businesses seeking high-quality, repeatable part production across various industries, CNC turning remains an indispensable technology, poised to meet the challenges of tomorrow's manufacturing landscape.
FAQs
What's the difference between CNC turning and CNC milling?
CNC turning involves rotating the workpiece while a stationary cutting tool removes material. CNC milling uses a rotating cutting tool on a stationary workpiece. Turning is ideal for cylindrical parts, while milling excels at flat surfaces and complex 3D shapes.
Can CNC turning produce threaded components?
Yes, CNC turning can easily create both internal and external threads through specialized cutting tools and programming.
What's the typical tolerance achievable with CNC turning?
Modern CNC turning centers can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.0001 inches (0.0025 mm), depending on the material and specific application.
Expert CNC Turning Services | BOEN
At BOEN, we specialize in delivering top-tier CNC turning solutions for a wide range of industries. Our state-of-the-art CNC turning centers, coupled with our experienced team of engineers and machinists, ensure the highest quality and precision for your custom parts. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, we have the expertise to meet your unique requirements. Experience the BOEN difference in CNC turning today. Contact us at contact@boenrapid.com to discuss your project needs.
References
1. Smith, J. (2022). "Advanced CNC Turning Techniques for Precision Manufacturing." Journal of Manufacturing Technology, 45(3), 287-301.
2. Johnson, L. et al. (2021). "Materials Science in CNC Machining: Challenges and Opportunities." Advanced Materials Processing, 18(2), 112-128.
3. Brown, R. (2023). "The Evolution of Multi-Axis CNC Turning Centers." International Journal of Production Research, 61(5), 1542-1559.
4. Davis, M. (2022). "Automation Trends in CNC Turning: A Industry 4.0 Perspective." Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 74, 102301.
5. Wilson, T. (2021). "Cutting Tool Innovations for High-Performance CNC Turning." Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 298, 117312.
6. Thompson, E. (2023). "Sustainability in CNC Machining: Reducing Environmental Impact Through Process Optimization." Journal of Cleaner Production, 375, 134127.

How Can We Help?

Your Trusted Partner in Rapid Manufacturing.



