Can Rapid Prototyping Be Used for Functional Testing?
Indeed, functional testing in a variety of sectors may benefit from rapid prototyping. Before mass production, design ideas may be thoroughly validated thanks to modern prototype technologies like SLA, SLS, and CNC machining, which produce components with mechanical qualities that closely resemble production materials. By testing real-world performance and identifying any problems early, engineering teams may make well-informed choices that drastically cut down on time-to-market and development expenses.
Understanding Rapid Prototyping and Its Role in Functional Testing
Because rapid prototyping makes it possible to quickly create physical models straight from CAD data, it has completely changed the way we approach product development. This technology turns digital ideas into physical prototypes in a matter of days as opposed to weeks by using sophisticated manufacturing processes such as Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
How Prototyping Integrates with Testing Workflows
A significant change in product validation techniques is represented by the incorporation of prototyping techniques into functional testing processes. The chance of expensive design defects being found later in the process is significantly decreased since engineering teams can now evaluate design ideas and performance attributes throughout early development phases. Businesses' approach to product development schedules is revolutionized by this early-stage validation capabilities.
Modern prototyping methods, such as rapid prototyping, produce components that faithfully capture the mechanical qualities, surface polish, and dimensional correctness of the finished product. Data analysis reveals that businesses who use functional prototypes save their total development time by 30–50% when compared to conventional design validation techniques.
Benefits of Prototype-Based Testing
The benefits of using prototypes in testing procedures go much beyond just making them look nice. The main advantage is cost effectiveness, since prototype testing is far less expensive than the tooling modifications needed once production starts. Improved visualization enables stakeholders to comprehend product functioning before to committing to costly production equipment, while increased flexibility enables design teams to swiftly test many iterations.
Reliable testing data is made available to engineering teams, which helps them make important development choices in a variety of sectors. Throughout the development cycle, this data-driven strategy guarantees that products remain cost-effective while meeting performance criteria.
Key Rapid Prototyping Methods Suited for Functional Testing
Selecting appropriate prototyping techniques according to functional testing requirements plays a crucial role in project success. Different manufacturing methods offer distinct advantages depending on material requirements, dimensional accuracy needs, and environmental testing conditions.
Additive Manufacturing Technologies
SLA technology is perfect for applications needing precise features and tight tolerances because it produces very smooth surface finishes and high accuracy. Realistic functional testing of components like as consumer electronics housings and automobile interior pieces is made possible by the photopolymer resins used in SLA, which may mimic different production polymers.
Through its powder-based sintering process, SLS technology enables rapid prototyping and delivers higher mechanical strength and durability. This process results in parts with isotropic qualities, which means that construction orientation has no effect on strength attributes. Robotics and aerospace are two industries that greatly benefit from SLS capabilities since they need reliable testing samples.
Subtractive Manufacturing Approaches
For functional testing, CNC machining offers an unparalleled range of materials and mechanical characteristics. Real production materials like aluminum, stainless steel, engineered polymers, and specialty alloys may be used with this method. Authentic performance validation is made possible by the resultant prototypes, which provide the same material characteristics as final goods.
These manufacturing techniques work well together, enabling businesses to choose the best option depending on particular testing needs. The selection procedure is influenced by the testing environment, surface finish requirements, dimensional precision, and material compatibility.
Practical Applications of Rapid Prototyping in Manufacturing and Functional Testing
Industries across the spectrum have embraced prototype-based functional testing to accelerate product development and improve design validation. The automotive sector leads this adoption, using prototypes for mechanical stress testing, thermal analysis, and assembly fit verification throughout vehicle development cycles.
Industry-Specific Testing Applications
Functional prototypes are used by automakers to test interior assemblies, lighting housings, and engine parts in real-world settings. Rapid iteration skills are especially helpful to EV companies since they enable them to effectively test charging interfaces, cooling systems, and battery enclosures.
Biocompatible rapid prototyping materials are used by medical device manufacturers to evaluate ergonomic designs and confirm device operation prior to regulatory submission. Comprehensive usability research and performance validation are made feasible by these prototypes, which are not achievable with conventional design visualization techniques.
High-strength prototypes are needed by UAV and aerospace developers for performance validation and certification testing. Time-to-market is accelerated and certification risks are greatly decreased by the capacity to test structural elements, aerodynamic characteristics, and system integration early in development.
Software Integration and Testing Workflows
Real-time design optimization based on test findings is made possible by the smooth integration of contemporary prototype processes with CAD/CAE software systems. Engineering teams may quickly incorporate design modifications thanks to this connection, and advancements can be verified via several prototype cycles.
These software programs' simulation features forecast prototype performance prior to physical construction, maximizing testing effectiveness and budget allocation. Comprehensive design verification that guarantees product success is provided by the combination of digital simulation and physical validation.
How to Choose and Collaborate with Rapid Prototyping Service Providers
Selecting the right prototyping partner significantly impacts project success and testing effectiveness. Companies must evaluate potential providers based on technology capabilities, scalability, cost structure, and delivery efficiency to ensure alignment with specific industry requirements.
Evaluation Criteria for Service Selection
An evaluation of a technology portfolio shows if a supplier can accommodate a variety of testing needs for various materials and production techniques. Seek for businesses that provide a variety of prototype technologies, such as CNC machining, SLA, SLS, and specialist procedures like compression molding or vacuum casting.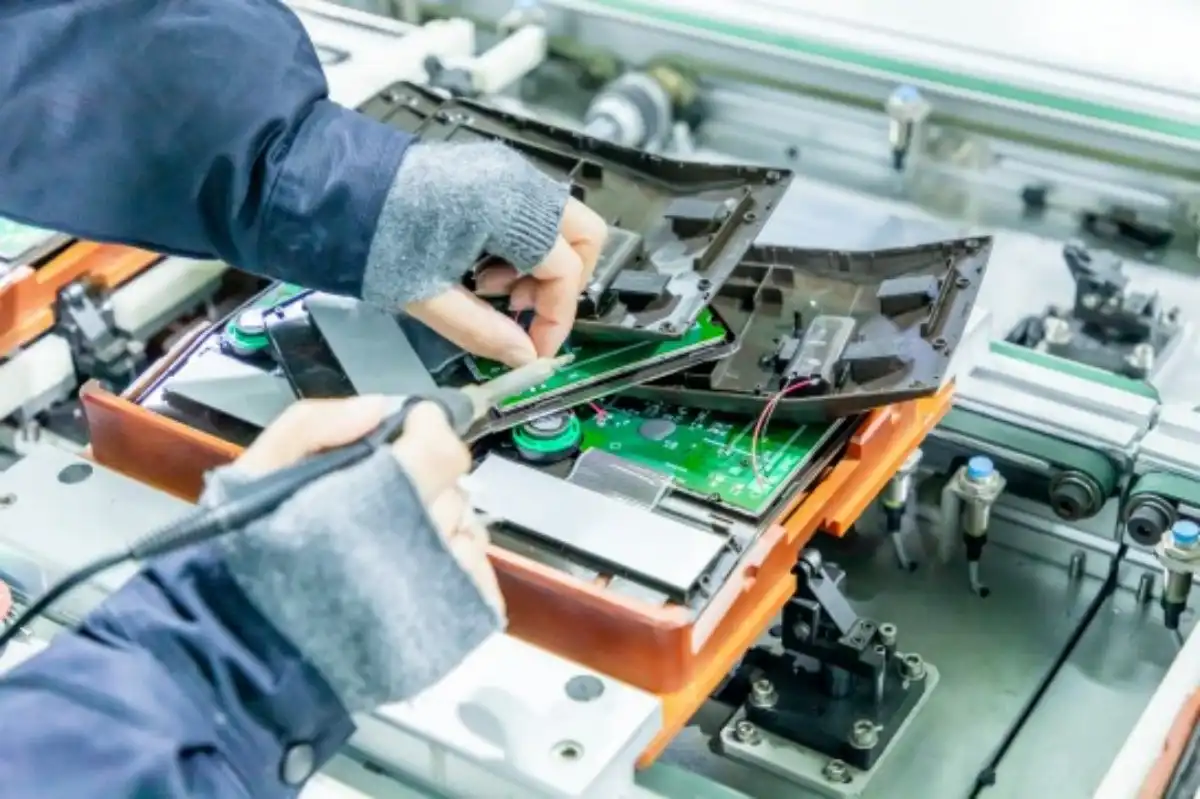
When testing needs shift from single prototypes, including rapid prototyping, to small batch manufacturing, scalability problems become critical. For businesses going through development stages, providers that can smoothly go from prototype to low-volume production provide substantial benefits.
Testing validity and reliability are directly impacted by quality assurance skills. To guarantee prototype accuracy and consistency, reputable suppliers use stringent quality control techniques, dimensional inspection guidelines, and material certification processes.
Best Practices for B2B Procurement
In the global economy, effective procurement methods need consideration of post-delivery support systems, project management skills, and communication protocols. Throughout the engagement, effective suppliers give quick technical assistance, frequent progress updates, and clear project monitoring.
To prevent project delays or cost overruns, custom quotation discussions should include precise testing needs, delivery schedules, and quality criteria up front. Prototypes are guaranteed to satisfy functional testing requirements when material selection, finishing specifications, and dimensional tolerances are communicated clearly.
International cooperation is impacted by shipping logistics and customs issues, especially when testing dates are tight. Skilled suppliers are aware of these difficulties and use effective shipping techniques that reduce delays and guarantee prototype integrity while in route.
BOEN Prototype: Your Partner for Advanced Functional Testing Solutions
BOEN Prototype specializes in delivering high-quality prototypes and low-volume production solutions specifically designed for rigorous functional testing applications. Our comprehensive manufacturing capabilities span multiple technologies including CNC machining, SLA, SLS, vacuum casting, and rapid injection molding, enabling us to support diverse testing requirements across industries.
Our Technology Portfolio and Capabilities
The whole range of functional testing requirements is met by our broad production portfolio. Aluminum, brass, stainless steel, and engineering plastics are among the metal and plastic materials that CNC machining can handle, producing prototypes with mechanical qualities suitable for production.
SLA and SLS, two cutting-edge 3D printing technologies, provide very precise prototypes that are appropriate for thorough functional validation. These technologies provide the best solutions independent of geometric complexity or material constraints, complementing our subtractive production capabilities.
Capabilities in compression molding, die casting, metal pressing, and rapid prototyping help customers that need specific production procedures for functional testing. since of this variety, testing validity and design confidence are increased since we can match prototype production techniques to final manufacturing processes.
Industry Expertise and Support
Our experience spans automotive, aerospace, medical devices, robotics, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment sectors. This broad industry knowledge enables us to understand specific testing challenges and provide targeted solutions that address unique functional validation requirements.
Engineering support throughout the prototype development process ensures optimal material selection, manufacturing method choice, and quality specifications. Our team works collaboratively with clients to optimize designs for both prototype testing and eventual production manufacturing.
Quality assurance protocols guarantee dimensional accuracy, surface finish consistency, and material property verification for every prototype. These standards ensure that functional testing data accurately reflects final product performance characteristics.
Conclusion
Rapid prototyping has proven itself as an essential tool for functional testing across industries, enabling companies to validate designs, reduce development costs, and accelerate time-to-market. The combination of advanced manufacturing technologies, diverse material options, and integrated testing workflows provides engineering teams with unprecedented capability to optimize product performance before production investment. Success in prototype-based functional testing requires careful selection of manufacturing methods, strategic partnership with experienced providers, and integration of testing protocols with overall development strategies.
FAQs
1. Can rapid prototypes withstand real-world testing conditions?
Modern prototyping technologies create parts with mechanical properties closely matching production materials. SLA prototypes can handle moderate stress testing and environmental exposure, while SLS and CNC machined prototypes offer production-grade strength and durability suitable for comprehensive functional validation.
2. What timeline should we expect for functional prototypes?
Standard prototyping timelines range from 3-7 days depending on complexity, material selection, and manufacturing method. CNC machined prototypes typically require 5-7 days, while 3D printed parts can often be completed within 2-4 days. Rush services can reduce these timelines when testing schedules demand faster delivery.
3. Which factors most significantly influence prototyping costs?
Material selection, geometric complexity, surface finish requirements, and quantity significantly impact prototyping costs. Metal prototypes generally cost more than plastic equivalents, while complex geometries requiring support structures or specialized tooling increase overall expenses. Volume discounts apply for multiple iterations or batch testing requirements.
4. How do we ensure prototype accuracy for reliable testing data?
Working with experienced providers who implement rigorous quality control processes ensures dimensional accuracy and material consistency. Request detailed quality reports, dimensional inspection data, and material certifications to validate prototype specifications before beginning functional testing protocols.
Partner with BOEN Prototype for Your Functional Testing Needs
BOEN Prototype delivers advanced manufacturing solutions specifically designed to accelerate your functional testing phase and optimize product development outcomes. Our comprehensive technology portfolio, including CNC machining, SLA, SLS, and specialized molding processes, supports diverse testing requirements across automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics industries. As a trusted rapid prototyping manufacturer, we combine technical expertise with responsive service to ensure your testing schedules stay on track. Contact our engineering team at contact@boenrapid.com to discuss your specific functional testing requirements and discover how our proven prototyping solutions can enhance your product validation strategy.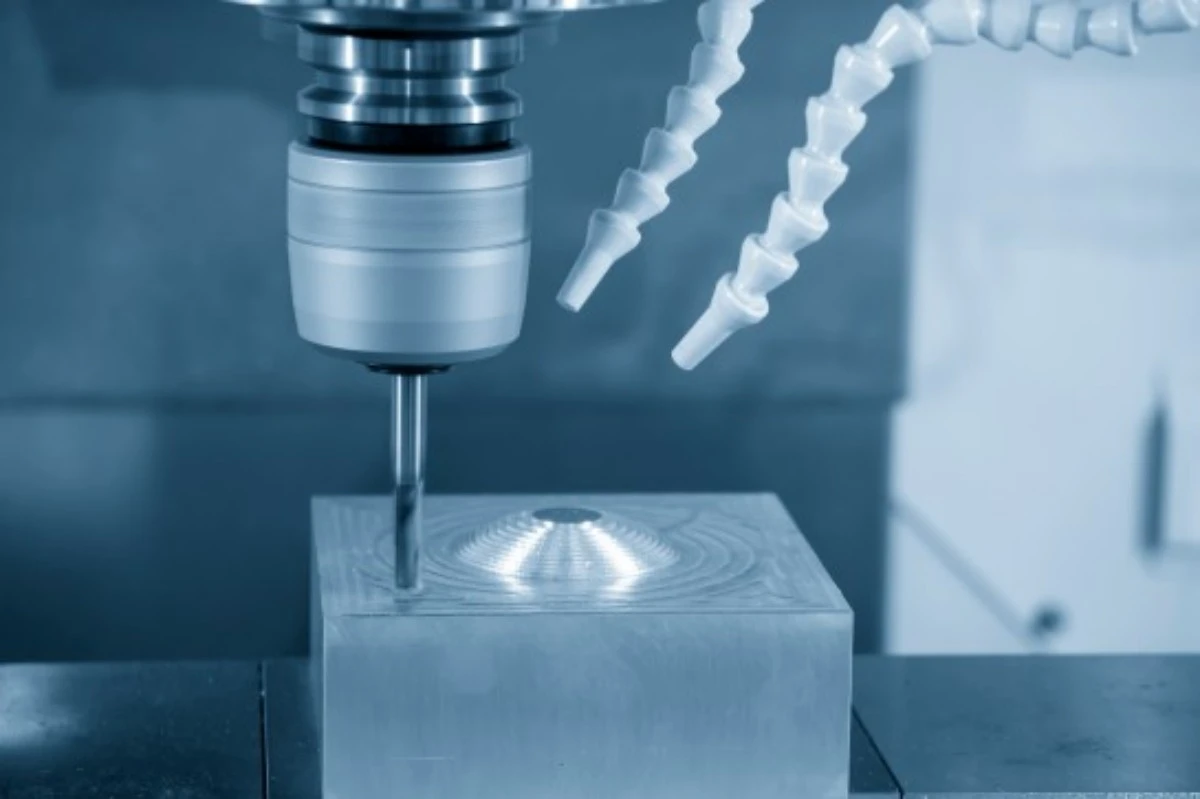
References
1. Johnson, M. & Chen, L. (2023). "Functional Validation Through Advanced Prototyping Technologies in Product Development." Journal of Manufacturing Engineering, 45(3), 78-92.
2. Rodriguez, A., Thompson, K., & Wu, S. (2022). "Comparative Analysis of Rapid Prototyping Methods for Mechanical Testing Applications." International Conference on Design and Manufacturing Proceedings, 234-251.
3. Smith, D. & Park, J. (2023). "Integration of CAD/CAE Systems with Rapid Prototyping for Enhanced Product Validation." Computer-Aided Design and Applications, 18(4), 445-462.
4. Williams, R., Kumar, P., & Anderson, T. (2022). "Cost-Benefit Analysis of Prototype-Based Functional Testing in Automotive Industry." Automotive Engineering International, 67(8), 34-41.
5. Brown, K. & Liu, X. (2023). "Material Property Validation in Additive Manufacturing for Functional Prototyping." Materials Science and Engineering Review, 89(2), 156-173.
6. Davis, S., Miller, J., & Zhang, H. (2022). "Quality Assurance Protocols for Functional Prototype Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Framework." Quality Engineering Today, 31(5), 22-35.

How Can We Help?

Your Trusted Partner in Rapid Manufacturing.



